active directory domain controller
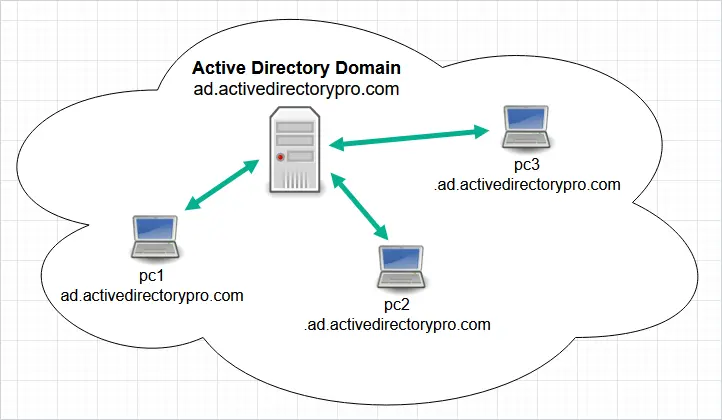
An Active Directory Domain Controller (AD DC) is a server that handles security authentication requests within a Windows Server domain. It is a crucial component of Active Directory, which is used to manage users, computers, and other resources in a networked environment. Here’s a detailed guide on Active Directory Domain Controllers, including their roles, features, and best practices.
1. Understanding Active Directory
- Active Directory (AD): A directory service developed by Microsoft for Windows domain networks. It provides a range of functions for managing and organizing network resources.
- Domain: A logical grouping of network objects (like users, computers, and devices) that share a common directory database and security policies.
2. Roles of Active Directory Domain Controller
- Authentication: AD DC authenticates users and computers within the domain, ensuring secure access to network resources.
- Authorization: It determines the permissions and access levels of users and groups to resources such as files, folders, and applications.
- Directory Services: Manages the directory information, including user accounts, groups, computers, and organizational units (OUs).
- Group Policy Management: Allows for the implementation of security and configuration policies across multiple computers and users within the domain.
3. Types of Domain Controllers
- Primary Domain Controller (PDC): The main controller in a domain responsible for managing all security authentication requests. In modern Windows Server environments, the PDC role has largely been replaced by the flexible architecture of AD.
- Backup Domain Controller (BDC): Historically, this was a secondary server that could handle authentication requests if the PDC was unavailable. In modern environments, all domain controllers are equal and can serve authentication requests.
4. Key Features of Active Directory Domain Controllers
- Replication: AD DCs replicate directory data among themselves to ensure consistency and redundancy across the domain.
- DNS Integration: AD relies on the Domain Name System (DNS) for locating domain controllers and other resources within the domain.
- Trust Relationships: Domain controllers can establish trust relationships with other domains, allowing users in one domain to access resources in another.
5. Deployment of Active Directory Domain Controller
5.1 Prerequisites
- Operating System: Ensure you have a compatible version of Windows Server (e.g., Windows Server 2019).
- Static IP Address: Assign a static IP address to the domain controller to ensure reliability.
- DNS Configuration: Properly configure DNS settings for the domain controller.
5.2 Installation Steps
Install Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS):
- Open the Server Manager, click on Add roles and features, and select Active Directory Domain Services.
Configure the Domain Controller:
- After installation, promote the server to a domain controller by running the Active Directory Domain Services Configuration Wizard.
- Choose to create a new domain or add the controller to an existing domain.
Set Up Domain Naming:
- Choose a domain name (e.g.,
example.local) and configure the forest and domain functional levels.
- Choose a domain name (e.g.,
Complete the Installation:
- After configuration, restart the server to complete the domain controller setup.
6. Best Practices for Managing Active Directory Domain Controllers
- Regular Backups: Schedule regular backups of AD DS to protect against data loss.
- Monitoring: Use monitoring tools to track the health and performance of domain controllers.
- Security Policies: Implement strong security policies, including password complexity requirements and account lockout policies.
- Replication Monitoring: Ensure that replication between domain controllers is functioning correctly to maintain consistency.
- Access Control: Limit administrative access to domain controllers to authorized personnel only.
Conclusion
Active Directory Domain Controllers play a vital role in managing user access, security, and resource allocation within a Windows network. By understanding their functions, features, and best practices, you can effectively deploy and manage AD DCs to enhance your organization’s IT infrastructure. Agajservices is equipped to assist with the implementation and management of Active Directory solutions tailored to your business needs.
